What Is an Inverse ETF and How It Works in 2025 | Complete Guide for Smart Investors
By CapitalKeeper | Beginner’s Guide | Indian Equities | Market Moves That Matter
Discover how inverse ETFs work, how they let investors profit from falling markets, and when to use them wisely. Learn the pros, cons, and risks of inverse ETFs in 2025.
🧭 Introduction: Turning Market Declines into Opportunities
In a world where markets move up and down faster than ever, smart investors are no longer limited to “buy low, sell high.” With tools like Inverse ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds), you can actually profit when the market falls.
Inverse ETFs, also called “short ETFs” or “bear ETFs,” are designed to move in the opposite direction of an underlying index or benchmark. So when the Nifty 50, S&P 500, or Bank Nifty goes down — the inverse ETF goes up.
For traders and investors seeking hedging, short-term profits, or portfolio protection, understanding how inverse ETFs work is essential in 2025’s volatile environment.
📈 What Is an Inverse ETF?
An Inverse ETF is a type of exchange-traded fund that aims to deliver the opposite performance of a given index or asset.
For example:
- If the Nifty 50 drops by 1%, an inverse Nifty ETF should rise by 1% (before fees and tracking errors).
- Conversely, if the index rises by 1%, the inverse ETF would fall by 1%.
These ETFs use derivative instruments such as futures, options, and swaps to achieve this inverse exposure.
👉 In simple terms, Inverse ETFs are designed to let investors “short the market” without using margin or directly short-selling stocks.
💡 How Do Inverse ETFs Work?
Inverse ETFs don’t directly own the stocks of the index they track. Instead, they use derivatives to bet against the index.
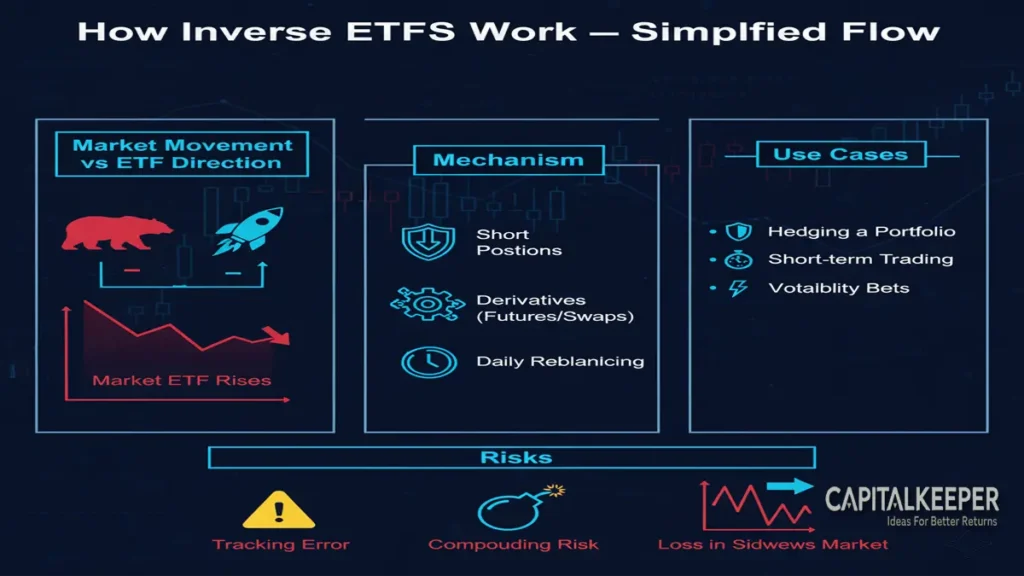
🔹 Step-by-Step Working Mechanism:
- Tracking a Benchmark Index:
The ETF selects a target index — for instance, Nifty 50, S&P 500, or a sector index like Nifty IT. - Using Derivatives:
The fund manager uses index futures, swaps, or options to gain short exposure to that index. - Daily Rebalancing:
The ETF resets its exposure daily, aiming to match the inverse of the index’s daily performance. - Return Calculation:
If the Nifty falls 2% today, an inverse ETF based on Nifty will gain approximately 2%. But if Nifty rises tomorrow, the ETF will lose value accordingly.
⚙️ Example:
If you buy ₹1,00,000 worth of an inverse Nifty ETF:
- Day 1: Nifty falls by 1% → ETF gains 1% → Value = ₹1,01,000
- Day 2: Nifty rises by 2% → ETF loses 2% → Value = ₹98,980
This daily compounding effect makes inverse ETFs suitable mainly for short-term trading rather than long-term holding.
⚠️ Why the Daily Reset Matters
The daily reset feature means inverse ETFs are designed to track daily percentage changes, not long-term performance.
Over time, this leads to a phenomenon called “compounding decay” — the ETF’s returns may diverge significantly from the inverse of the index’s long-term performance.
Example:
If an index rises 10% one day and falls 10% the next, it ends up at -1% overall.
But an inverse ETF tracking it would lose more than 1% due to daily compounding.
👉 Key takeaway: Inverse ETFs are ideal for short-term tactical plays, not for buy-and-hold strategies.
🧠 Why Do Investors Use Inverse ETFs?
Inverse ETFs serve multiple purposes — not just speculation.
1️⃣ Hedging a Portfolio
Investors use inverse ETFs to protect portfolios during expected market downturns.
Example:
If you hold long-term positions in large-cap stocks but expect a short-term correction, buying an inverse ETF on Nifty can offset potential losses.
2️⃣ Short-Term Trading Opportunities
Traders often use inverse ETFs to profit from temporary market corrections without using futures or margin accounts.
3️⃣ Avoiding Short Selling Risks
Traditional short selling requires borrowing shares and paying interest or margin costs. Inverse ETFs simplify this process — you can “short” by simply buying the ETF through your regular trading account.
📊 Types of Inverse ETFs
There are several categories of inverse ETFs based on exposure type and leverage:
🔸 1. Standard Inverse ETFs (1x)
- Move 1x inverse to the index’s daily return.
- Example: If Nifty 50 drops 1%, the ETF rises 1%.
- Suitable for conservative hedging or tactical exposure.
🔸 2. Leveraged Inverse ETFs (–2x or –3x)
- Designed to deliver –2x or –3x the daily performance of the index.
- Example: A –2x Nifty ETF would rise 2% if Nifty drops 1%.
- High-risk, short-term instruments used by traders for quick profits.
🔸 3. Sector or Commodity Inverse ETFs
- Target specific sectors (like IT, Metals, Financials) or commodities (like Gold, Crude Oil).
- Example: An inverse crude oil ETF profits when oil prices fall.
💰 Benefits of Investing in Inverse ETFs
Inverse ETFs can be powerful when used wisely.
✅ 1. Simple Way to Profit from Market Downturns
You can capitalize on falling markets without shorting or using derivatives directly.
✅ 2. Effective Hedging Tool
Portfolio managers and individual investors use inverse ETFs to reduce downside exposure during uncertain or volatile phases.
✅ 3. Easily Tradable Like Stocks
Inverse ETFs trade on exchanges throughout the day, offering liquidity and transparency, just like equity ETFs.
✅ 4. No Margin or Borrowing Needed
You don’t need margin accounts, collateral, or stock borrowing — unlike traditional short selling.
⚠️ Risks and Limitations of Inverse ETFs
Despite their advantages, inverse ETFs come with notable risks — especially for beginners.
❌ 1. Daily Rebalancing and Compounding Risk
Because inverse ETFs reset daily, their long-term returns may deviate from expectations if held over multiple days.
❌ 2. Not for Long-Term Holding
These are trading instruments, not long-term investments. Holding them for weeks or months can lead to significant tracking errors.
❌ 3. Volatility Erosion
In volatile markets, the value of an inverse ETF can decay over time, even if the index ends at the same level.
❌ 4. Leverage Risk
Leveraged inverse ETFs magnify both gains and losses. A small move in the index can lead to disproportionately large losses in leveraged products.
🧩 Practical Example: Nifty 50 Inverse ETF
Let’s take an example based on Indian markets.
Suppose an investor expects the Nifty 50 to decline due to global uncertainty or weak earnings.
They can buy an inverse ETF like Nippon India Nifty 50 Inverse ETF.
If Nifty falls 2% in a day, the ETF would rise approximately 2%.
However, if Nifty rebounds the next day, the ETF will lose a similar amount — meaning timing and holding period are critical.
🔮 When Should You Use Inverse ETFs in 2025?
With global markets becoming more uncertain — elections, interest rate shifts, and AI-driven volatility — 2025 is shaping up to be a trader’s market.
Inverse ETFs can play a valuable role if used strategically:
📆 Short-Term Hedging:
Use them to protect profits during expected short-term corrections or events (like budget announcements or earnings season).
⚖️ Tactical Allocation:
Deploy small positions (5–10% of your portfolio) as a hedge against long positions during volatile phases.
🧩 Diversified Strategy:
Combine inverse ETFs with standard ETFs to create a market-neutral or risk-adjusted portfolio.
🧭 Tips for Trading or Investing in Inverse ETFs
- Track the Benchmark: Always know which index the ETF inversely tracks (e.g., Nifty 50, S&P 500).
- Use Stop-Losses: Protect yourself from sudden market rebounds.
- Avoid Long Holding Periods: Reset positions daily or weekly if needed.
- Monitor Expense Ratios: High management fees can erode returns.
- Start Small: Begin with a small capital allocation to understand volatility impact.
📚 Key Takeaways
| Factor | Inverse ETF |
|---|---|
| Objective | Profit when market falls |
| Mechanism | Uses futures, swaps, options |
| Holding Period | Short-term (1–5 days ideal) |
| Risk Level | High |
| Leverage | Optional (1x, 2x, 3x) |
| Best Use | Hedging, tactical trading |
| Unsuitable For | Long-term investors |
🧠 Conclusion: The Smart Investor’s Bear Market Tool
Inverse ETFs offer a powerful, simplified way to benefit from falling markets or hedge existing positions. They allow investors to stay active and protected even when the market mood turns bearish.
However, their strength lies in discipline and timing — they are not “buy and forget” instruments. Misusing them or holding them too long can lead to losses despite correct market calls.
For investors in 2025, the key is to use inverse ETFs as a defensive and tactical tool, not as a replacement for long-term investment strategies.
Inverse ETFs are not about predicting the market — they’re about protecting your capital when the market moves against you.
📌 For daily trade setups, technical learning, and smart investing tips, stay tuned to CapitalKeeper.in
📌 For more real-time updates, trade setups, and investment insights — follow us on [Telegram] and [WhatsApp Channel] subscribe to our newsletter!

Subscribe Now , Join Telegram the Crypto Capital Club, Get Free Crypto Updates
📌 Disclaimer
The content provided on CapitalKeeper.in is for informational and educational purposes only and does not constitute investment, trading, or financial advice. While we strive to present accurate and up-to-date market data and analysis, we make no warranties or representations regarding the completeness, reliability, or accuracy of the information.
Stock market investments are subject to market risks, and readers/investors are advised to conduct their own due diligence or consult a SEBI-registered financial advisor before making any investment decisions. CapitalKeeper and its authors are not liable for any loss or damage, direct or indirect, arising from the use of this information.
All views and opinions expressed are personal and do not reflect the official policy or position of any agency or organization. Past performance is not indicative of future results.By using this website, you agree to the terms of this disclaimer.
Ranjit Sahoo
Founder & Chief Editor – CapitalKeeper.in
Ranjit Sahoo is the visionary behind CapitalKeeper.in, a leading platform for real-time market insights, technical analysis, and investment strategies. With a strong focus on Nifty, Bank Nifty, sector trends, and commodities, she delivers in-depth research that helps traders and investors make informed decisions.
Passionate about financial literacy, Ranjit blends technical precision with market storytelling, ensuring even complex concepts are accessible to readers of all levels. Her work covers pre-market analysis, intraday strategies, thematic investing, and long-term portfolio trends.
When he’s not decoding charts, Ranjit enjoys exploring coastal getaways and keeping an eye on emerging business themes.
📌 Follow Ranjit on:
LinkedIn | Twitter/X | Instagram | ✉️ contact@capitalkeeper.in












Leave a Reply