Interest Rate Parity (IRP) Explained: Meaning, Types, and Real-World Applications
By CapitalKeeper | Pre Market Opening | Indian Equities | Market Moves That Matter
Interest Rate Parity (IRP): Definition, Types, and Applications
Learn what Interest Rate Parity (IRP) is, its covered and uncovered types, and how traders and investors use IRP to price currencies and manage risk.
Introduction
Currency markets are influenced by multiple economic factors, and one of the most critical relationships is the Interest Rate Parity (IRP). This concept helps traders, investors, and corporates understand how interest rate differentials between two countries impact exchange rates and arbitrage opportunities.
Whether you’re trading forex, hedging international exposure, or analyzing macroeconomic conditions, IRP forms the backbone of currency pricing models.
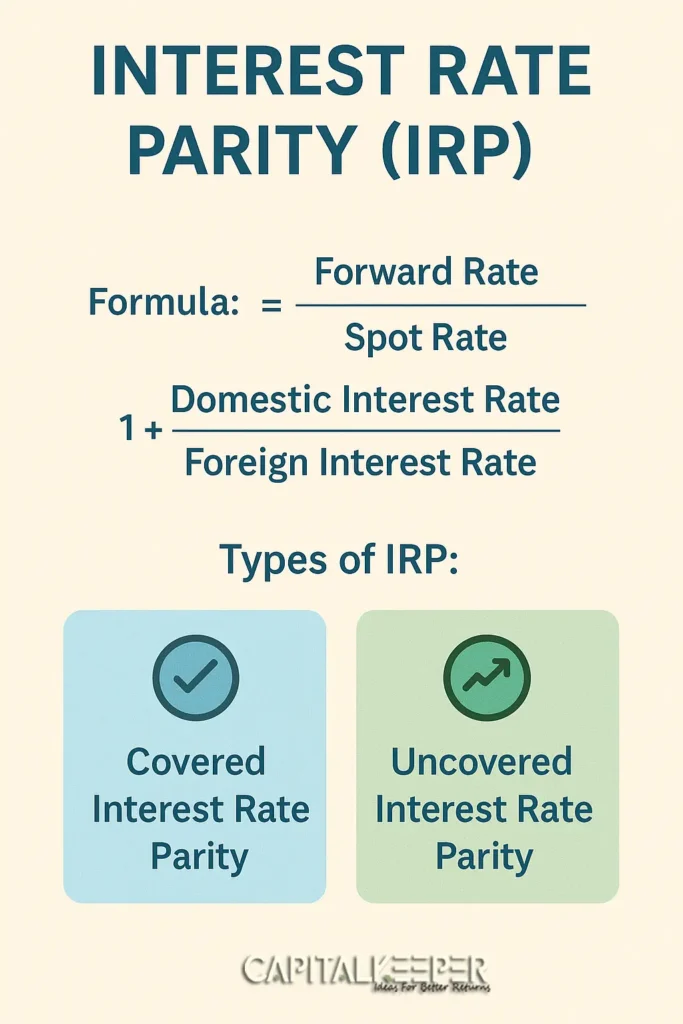
What is Interest Rate Parity (IRP)?
Interest Rate Parity (IRP) is a fundamental theory in foreign exchange markets that states:
The difference between the interest rates of two countries is equal to the expected change in exchange rates between their currencies.
In simpler terms, IRP ensures there is no arbitrage opportunity (risk-free profit) in currency markets.
Formula for IRP: Forward RateSpot Rate=(1+Domestic Interest Rate)(1+Foreign Interest Rate)\frac{Forward\ Rate}{Spot\ Rate} = \frac{(1 + Domestic\ Interest\ Rate)}{(1 + Foreign\ Interest\ Rate)}Spot RateForward Rate=(1+Foreign Interest Rate)(1+Domestic Interest Rate)
Where:
- Spot Rate = Current exchange rate
- Forward Rate = Agreed rate for future transaction
- Domestic/Foreign Interest Rates = Rates in respective countries
Types of Interest Rate Parity
IRP is broadly classified into two types:
1. Covered Interest Rate Parity (CIRP)
- CIRP holds when forward exchange contracts are used to hedge risk.
- No arbitrage exists because forward rates already factor in interest rate differentials.
- Example: If U.S. and India interest rates differ, the forward USD/INR rate adjusts so traders cannot profit risk-free.
2. Uncovered Interest Rate Parity (UIRP)
- UIRP assumes no forward contract is used.
- Expected changes in future spot rates should equal the interest rate differential.
- However, UIRP often fails empirically due to market volatility and investor risk preferences.
Real-World Applications of IRP
1. Currency Hedging
- Corporates use CIRP to lock exchange rates and avoid currency risk on imports/exports.
2. Arbitrage Trading
- Traders exploit deviations from IRP (known as “carry trades”) when forward rates misalign with interest differentials.
3. Forecasting Exchange Rates
- Analysts apply UIRP to predict future currency movements based on interest rate outlooks.
4. Central Bank Policy Analysis
- IRP helps evaluate monetary policy impacts on currency value and capital flows between countries.
Example of Interest Rate Parity
- Spot Rate (USD/INR): 83.00
- U.S. Interest Rate: 4%
- India Interest Rate: 6%
- Forward Period: 1 year
Forward Rate=83×1+0.041+0.06=83×0.9811=81.43\text{Forward Rate} = 83 \times \frac{1+0.04}{1+0.06} = 83 \times 0.9811 = 81.43Forward Rate=83×1+0.061+0.04=83×0.9811=81.43
Thus, the 1-year forward USD/INR rate should be around ₹81.43, aligning with IRP.
Limitations of IRP
- Transaction costs and capital controls may prevent perfect parity.
- UIRP often deviates in real markets due to speculative flows and risk premiums.
- Geopolitical events can cause sudden currency mispricing.
Conclusion
Interest Rate Parity is a cornerstone of forex theory that links interest rates and currency exchange rates. While perfect parity rarely exists due to market imperfections, understanding IRP helps traders, corporates, and policymakers make informed decisions in a global financial landscape.
Monitoring IRP deviations can also reveal carry trade opportunities and potential risks in currency markets.
📌 For daily trade setups, technical learning, and smart investing tips, stay tuned to CapitalKeeper.in
📌 For more real-time updates, trade setups, and investment insights — follow us on [Telegram] and [WhatsApp Channel] subscribe to our newsletter!

📌 Disclaimer
The content provided on CapitalKeeper.in is for informational and educational purposes only and does not constitute investment, trading, or financial advice. While we strive to present accurate and up-to-date market data and analysis, we make no warranties or representations regarding the completeness, reliability, or accuracy of the information.
Stock market investments are subject to market risks, and readers/investors are advised to conduct their own due diligence or consult a SEBI-registered financial advisor before making any investment decisions. CapitalKeeper and its authors are not liable for any loss or damage, direct or indirect, arising from the use of this information.
All views and opinions expressed are personal and do not reflect the official policy or position of any agency or organization. Past performance is not indicative of future results.By using this website, you agree to the terms of this disclaimer.
Ranjit Sahoo
Founder & Chief Editor – CapitalKeeper.in
Ranjit Sahoo is the visionary behind CapitalKeeper.in, a leading platform for real-time market insights, technical analysis, and investment strategies. With a strong focus on Nifty, Bank Nifty, sector trends, and commodities, she delivers in-depth research that helps traders and investors make informed decisions.
Passionate about financial literacy, Ranjit blends technical precision with market storytelling, ensuring even complex concepts are accessible to readers of all levels. Her work covers pre-market analysis, intraday strategies, thematic investing, and long-term portfolio trends.
When he’s not decoding charts, Ranjit enjoys exploring coastal getaways and keeping an eye on emerging business themes.
📌 Follow Ranjit on:
LinkedIn | Twitter/X | Instagram | ✉️ contact@capitalkeeper.in













Leave a Reply